The isolator is installed between the tails of the meter and the consumer unit. The function of an isolator is to disconnect the supply from the meter to the consumer unit.
This is a safety feature which allows for the whole of an installation to be isolated from the incoming supply. Alternatively the main fuse would need to be removed by the DNO.
Unlike a switch, an isolator is not designed to disconnect the supply when "on load", ie when current is flowing through it. Double-pole refers to the ability to isolate both the line and neutral conductors.

The consumer unit connects to the incoming supply and is used to divide an installation's circuits and provide protection against overcurrents, short-circuits and earth faults. The image below shows a consumer unit with some protective devices installed. Click on the tabs above to learn about each part. Note that the consumer unit is constructed of metal.
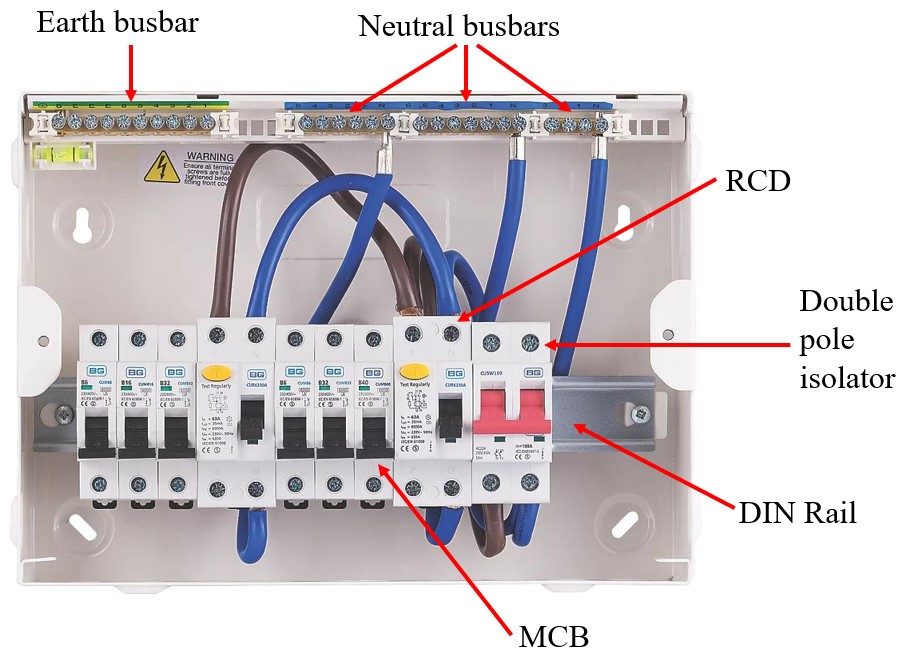
The main switch is found within the consumer unit. It is used to isolate the rest of the consumer unit from the mains supply.
It is a double pole isolator which means that both the line and neutral conductors are activated together simultaneously.
As an isolator it is not intended to be operated when the circuit is carrying current.

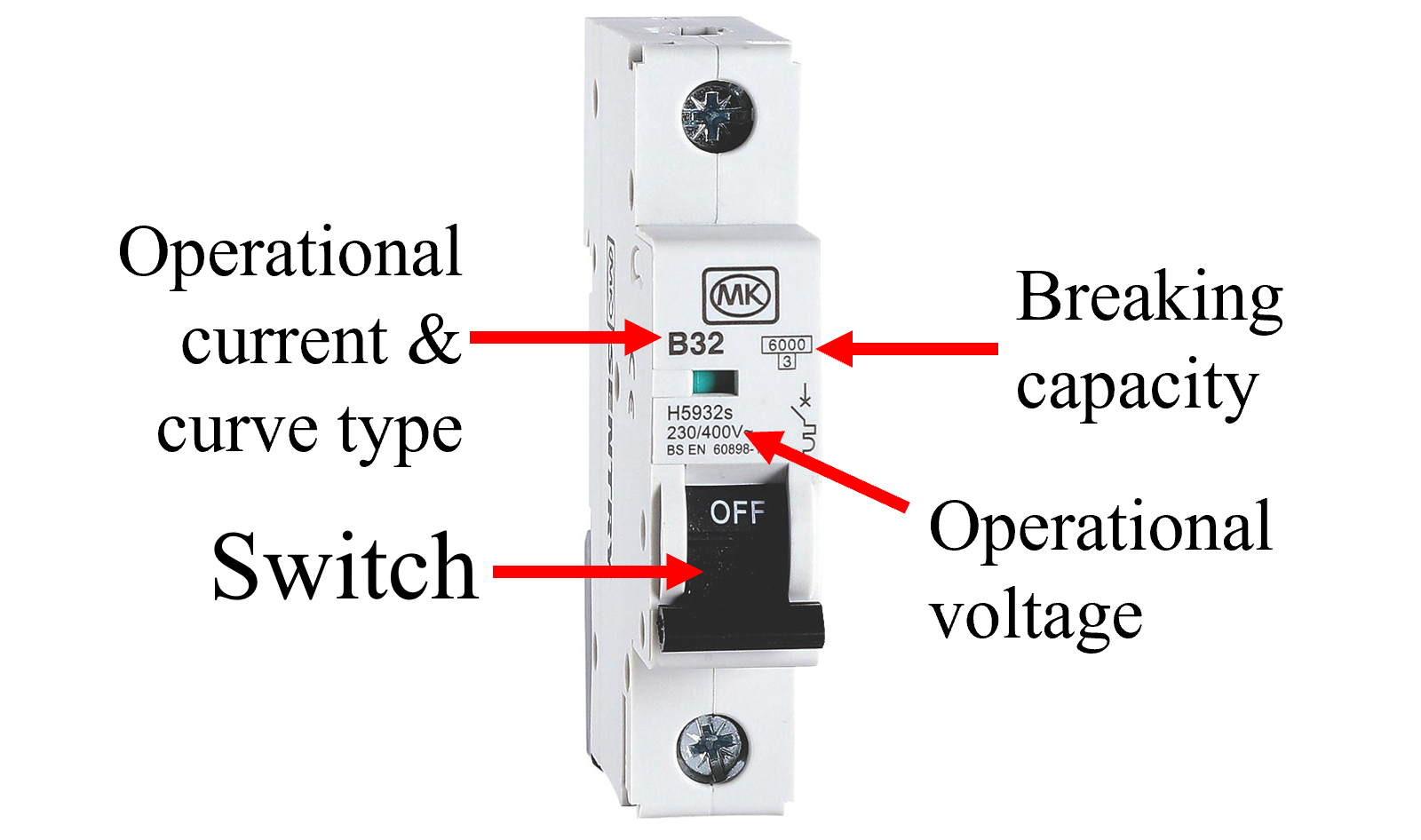
An MCB protects a circuit against short circuits and over-current conditions. An MCB is a single pole device and only disconects the line terminal should a fault occur.
B32 - The B is the curve type and the 32 is the operational current in amps.
The breaking capacity is the maximum fault current that can occur without the MCB becoming inoperable. It is 6000
A (6 kA) in this example.
The operational voltage is the voltage it is intended to operate at, in this case 230/400 V.

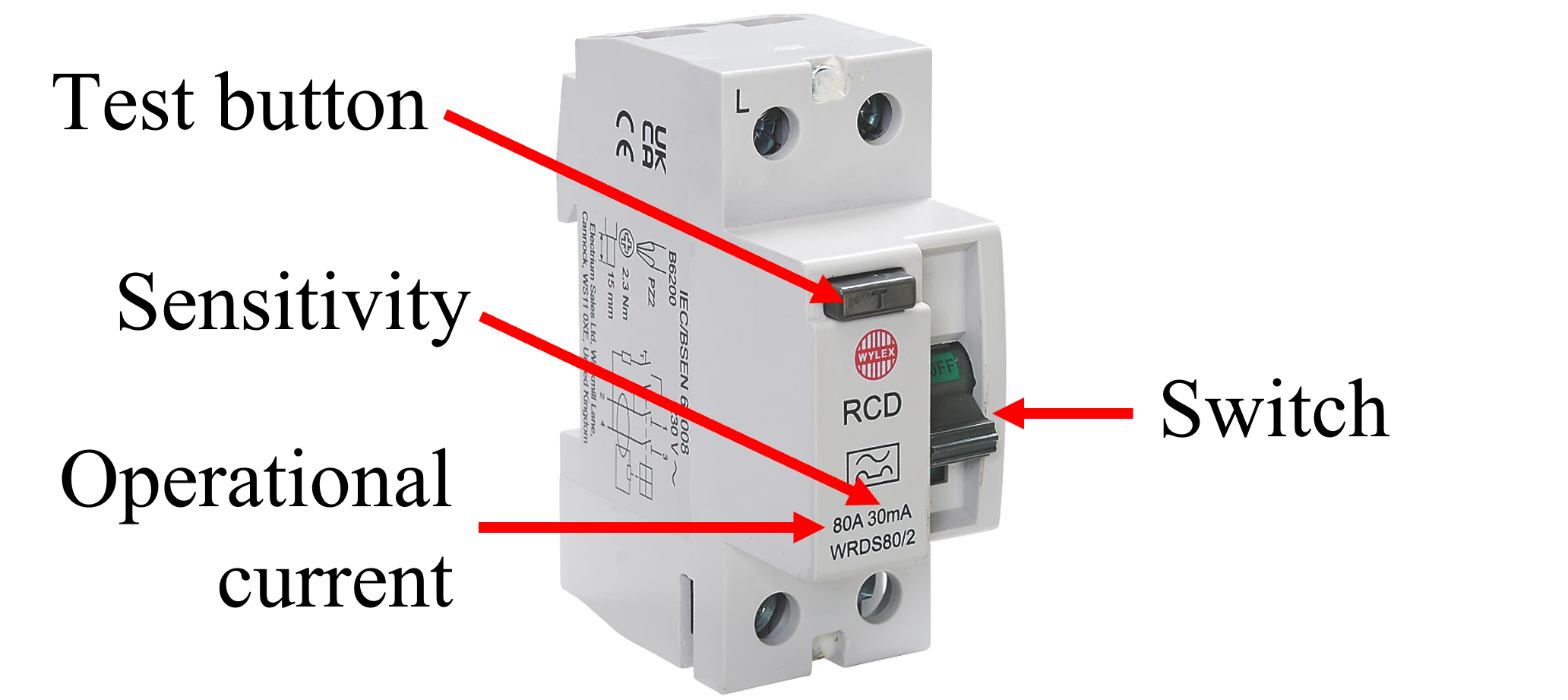
An RCD monitors the line and neutral currents, which under normal circumstances should be the same. If a fault occurs (such as a person coming into contact with a live terminal) an imbalance between the two currents occurs because an aditional path for current has been introduced. The RCD detects this imbalance and disconnects the supply. The RCD is a double-pole switch which means both the line and neutral terminals are disconnected.
The RCD shown has a sensitivity of 30 mA which is the imbalance required to cause the device to disconnect the supply.
The operational current is the maximum current that the RCD is designed to operate, in this cas 80 A .
The RCD can be tested by pressing the test button which introduces a resistor between the incoming line and outgoing neutral terminals, simulating a fault.
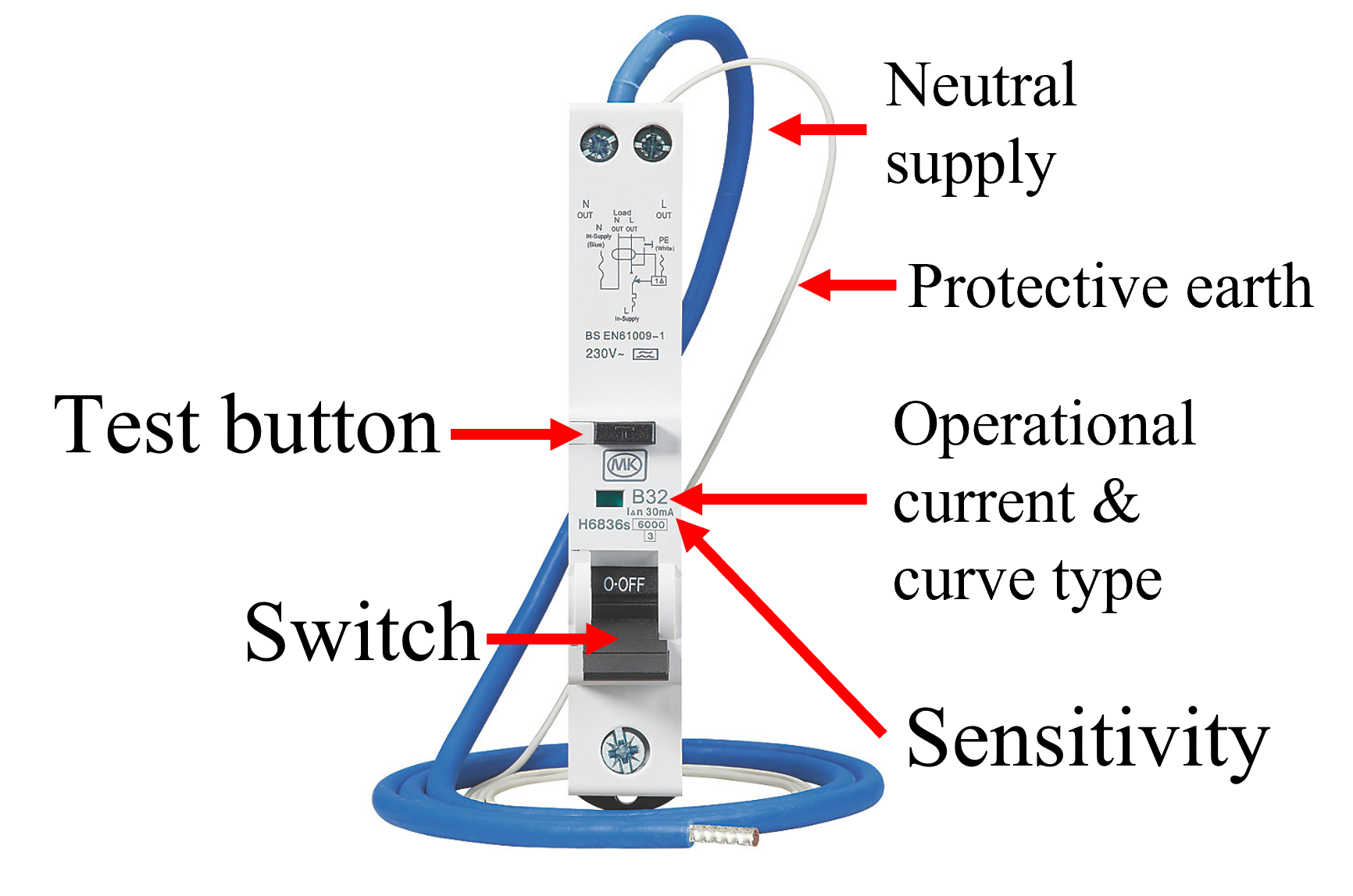
An RCBO combines the function of an RCD and an MCB in one device. They have the advantage that an earth fault on one circuit will not cause any other circuits to be disconnected.
Two additional cables are required as shown in the diagram.
As with an RCD the RCBO includes a test button.

BS3036 is a semi-enclosed rewirable fuse. The fuse wire can be replaced should it rupture (blow) because of a fault condition. The fuse wire is housed inside a ceramic tube and secured via two screws.
These fuses have the disadvantages:
* The incorrect fuse wire can be accidentally or deliberately be installed
* They have low breaking capacity
* The fuse wire degrades over time


A BS88 fuse is a type of cartridge fuse, consisting of a metal wire housed within a cylindrical ceramic tube. They are used to protect high power and industrial circuits. They have the following characteristics:
* High breaking capacity
* High nominal current values available
* Good discrimination
BS88-2: Used in industrial environments.
BS88-3: Used in domestic environments.
BS88-4: Use for motor controllers and drivers.
gG types are used for protection of general circuits.
gM types are used for protection of motor circuits.
This is a 25A general purpose (gG) BS88-2 fuse with a breaking capacity of 80 kA

