Capacitors are electronic components whose function it is to store electric charge. Fundamentally they consist of two metal plates seperated by an insulating material known as a dialectric.
The unit of capacitance is the Farad. The Farad is a large unit however, generally we talk in terms of micro farads (µF), nano farads (nF) and picofarads (pF).
1µF = 1x10-6 Farads
1nF = 1x10-9 Farads
1pF = 1x10-12 Farads
Capacitors are found in almost all electronic circuits as elements of timers, filters, power supply and oscillators.

Electrolytic capacitor

Ceramic capacitor

Electrolytic capacitor symbol

Capacitor symbol
Polyester capacitors come in a range of different shapes and sizes but are all fundamentally similar. They all consist of length polyester film that is sandwiched between thin metal films that form the electrodes.
This structure is then rolled up and sealed within some form of insulating material.
It is not always easy to determine the capacitance value or working voltage so some examples are shown here. In all of these examples the K indicates the type of dielectric.

0.47uF or 470nF 250V

10 nF 100V

0.1uF or 100nF 63 V

100nf 100V

2.2uF 50V
Ceramic capacitors are made by sanwitching layers of aluminium film and a ceramic insulating material.
They are generally used in applications where only a small capacitance is required. Ceramic capacitors can be manufactured to have very high working voltages well over 1000V.
They are low cost but suffer from poor stability.
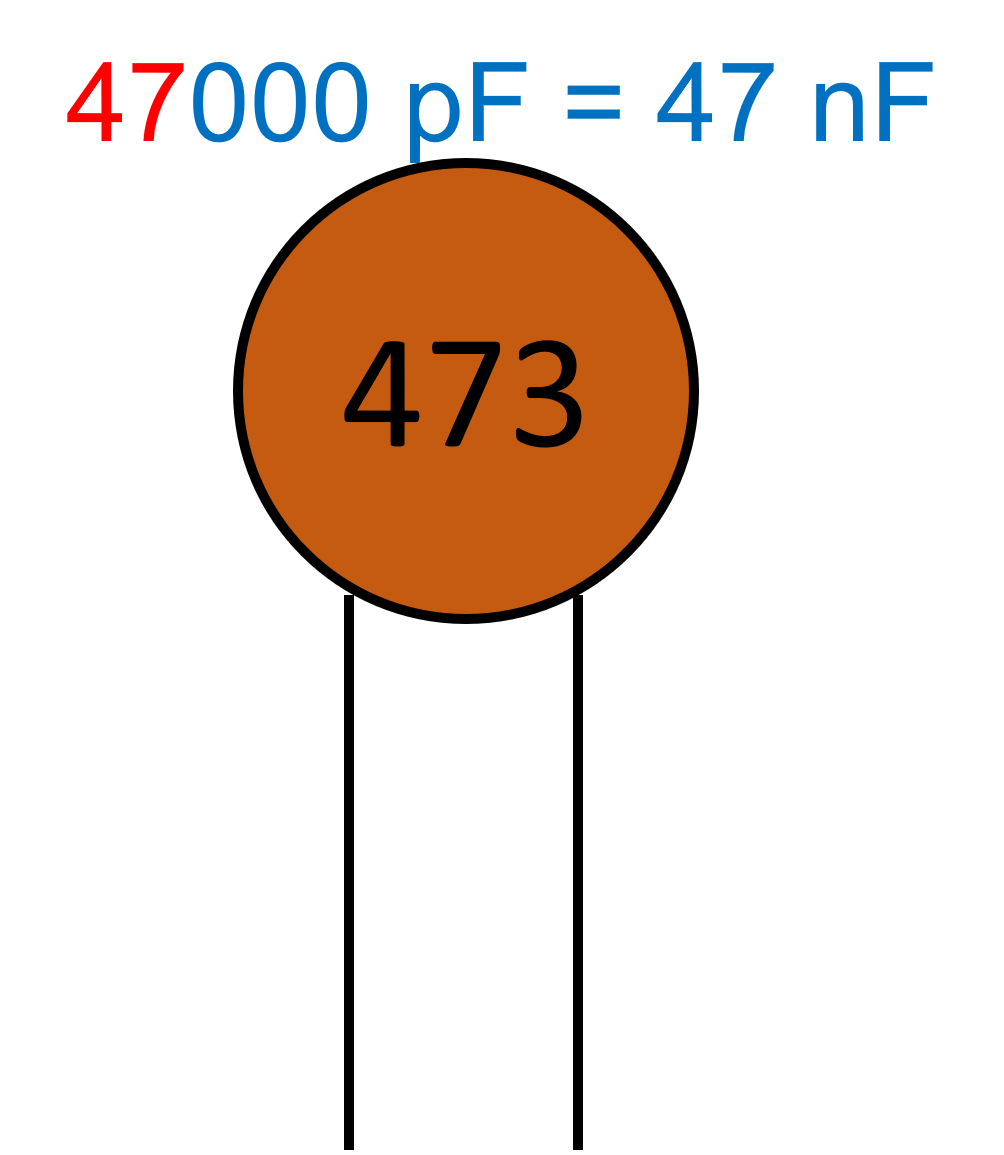
These capacitors are usually in the range of pico farads (very small). They are identified by reading the codes. The first two digits give you a value and the third digit tells you how many zeros to add onto the end.
An 18pF Ceramic capacitor




Electrolytic capacitors have the great advantage of being able to achieve much greater capacitance values than the other types mentioned so far. This is commonly in the microfarad range.
Modern capacitors can now be manufactured to have capacitances of many Farads, which is a huge value. These "super capacitors" are used in some hybrid electric cars.
Electrolytic capacitors usually contain a liquid electrolyte. They are polarised, which means that they must be connected with the correct polarity. If they are connected incorrectly, or a voltage greater than the working voltage is applied ,then heat is generated which boils the electrolyte causing it to explode.
These capacitors are easy to read as their values are usually printed clearly and are generally physically larger.
47uF 450V

