Batteries rely on the effect that electricity has on chemical reactions. The images show a conventional car battery and the batteries of an electric car.


Electroplating is the process of transfering one metal onto the surface of another. For example plating copper terminals with gold to prevent corrosion.


Hydrogen fuel cells convert oxygen and hydrogen gasses directly into DC electricity using a catalyst.

Whenever an electric current flows through a conductor with resistance heat is produced as electronc collide with metal atoms. Electrical energy is therefore converted to heat energy.
This is helpful when we want to make heat producing devices such as heaters and kettles. The image below shows an electric hot water tank element.

All cables have some resistance and as such heat up as current flows through them. This is why it is important to ensure that an electrical installation is designed to prevent cables overheating and starting a fire.
The image shown here demonstrates an overloaded thermostat.

A current flowing through a conductor will always produce a magnetic field around it. This is a very useful property and is the principle of operation of motors, alternators and transformers.
Motors are electrical machines that convert electrical energy into kinetic energy. Below is a three phase induction motor.

Transformers use electromagnetism to convert voltages. They are used in the National Grid to increase and decrease the voltage at various parts of the transmission and distribution network.
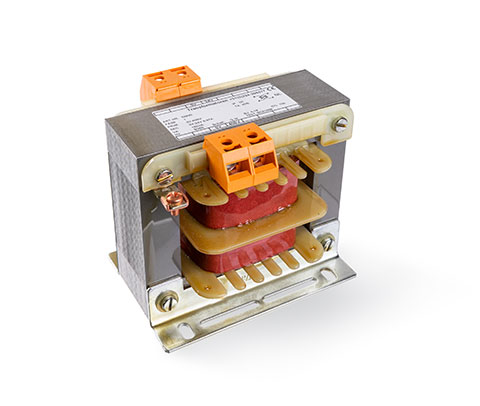
Most pieces of electronic equipment that connects to the mains supply has some form of transformer inside. They are used to reduce the voltage supplied to the equipment, an example is shown below.

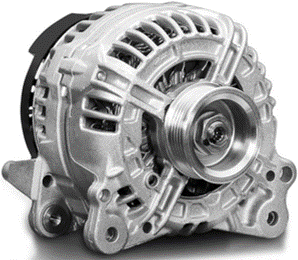
An alternator is an electrical machine that generates an alternating current when its shaft is rotated. They are used in cars to charge the battery, wind turbines and power stations. The image below is of a car alternator.
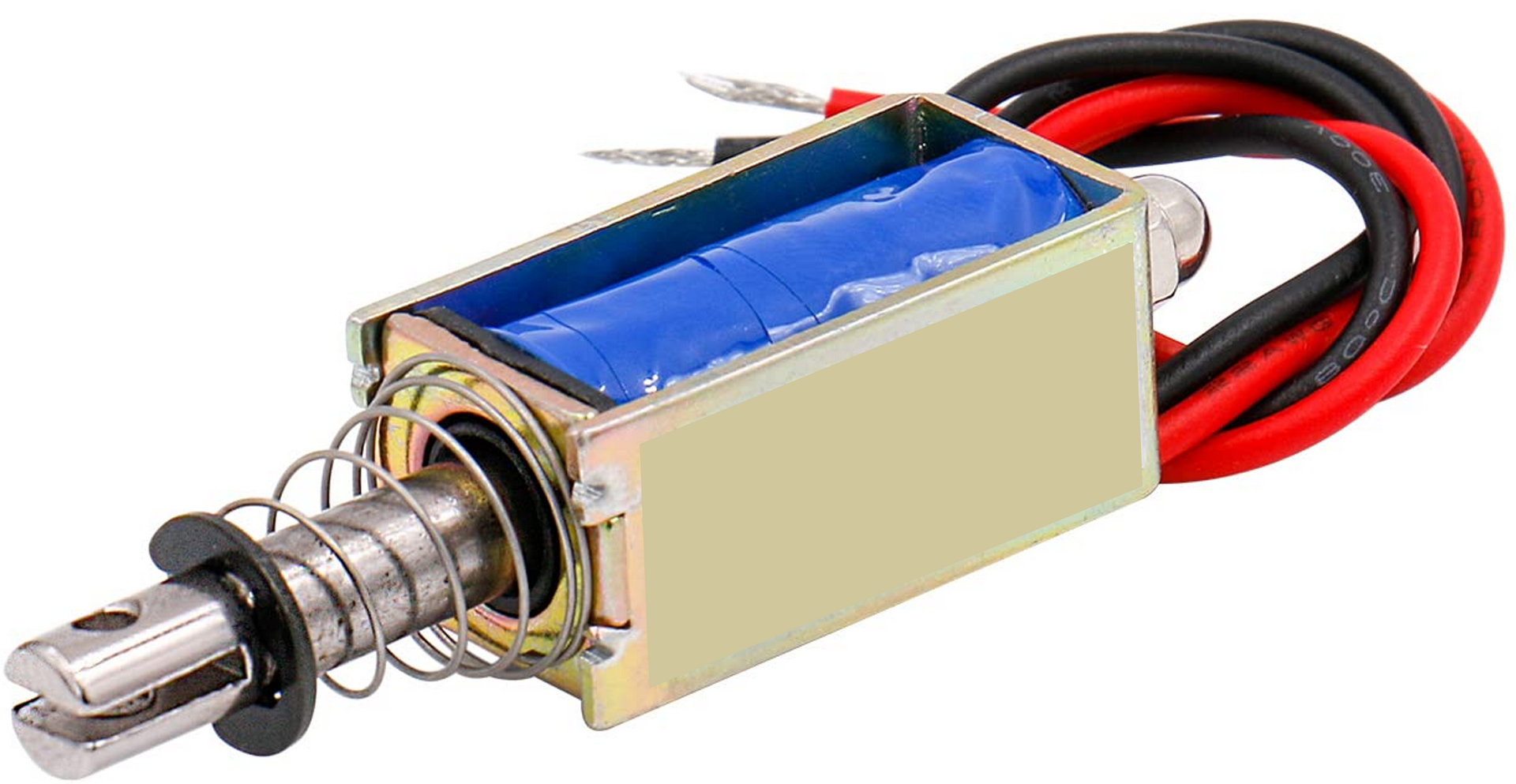
A solenoid converts electrical energy into linear motion. In the example below, the metal pin is pushed outwards by the spring. When current flows through the coil of wire inside, the magnetic field pulls the metal rod inwards.